Keypoints
What is Convolution?
- Convolution is one of the main building blocks of a CNN.
- The term convolution refers to the mathematical combination of two functions to produce a third function.
- It merges two sets of information. In the case of a CNN, the convolution is performed on the input data with the use of a “filter” or “kernel”(these terms are used interchangeably) to then produce a “feature map”.
What are Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)?
- We see and learn to recognize objects. An algorithm can also do the same provided that we teach it with millions of images so that it can learn to generalize and make predictions.
- But the way the computer perceives the images is much different than we do.
- A computer perceives the images in the form of numbers and any image can be represented as 2-dimensional arrays of numbers, known as pixels. To teach an algorithm to recognize objects in images, we use a specific type of Artificial Neural Network called a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN).
- Their first Convolutional Neural Network was called LeNet-5 and was able to classify digits from hand-written numbers.
- In a regular Neural network, the network transform an input by putting it through a series of hidden layers.
- Every layer is made up of a set of neurons, where each layer is fully connected to all neurons in the layer before. Finally, there is a last fully-connected layer, the output layer that represent the predictions.
- In a Convolutional Neural Network, the layers are organized in 3 dimensions aka width, height and depth.
- Further, the neurons in one layer do not connect to all the neurons in the next layer but only to a small region of it. Lastly, the final output will be reduced to a single vector of probability scores, organized along the depth dimension.
Regular NN vs CNN
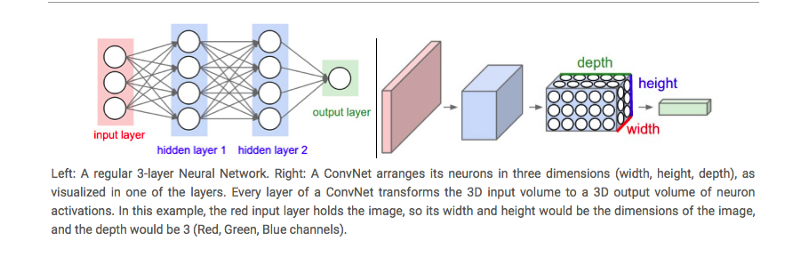 Image Credits1
Image Credits1
Architecture of a CNN
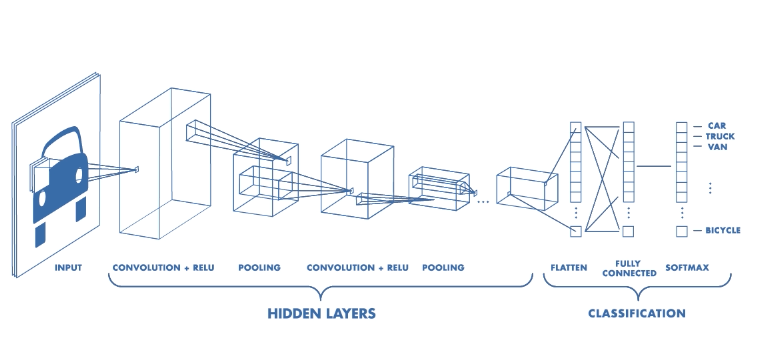
CNN has two components:
- Hidden Layers/Feature Extraction part
- Classification part.
Feature Extraction
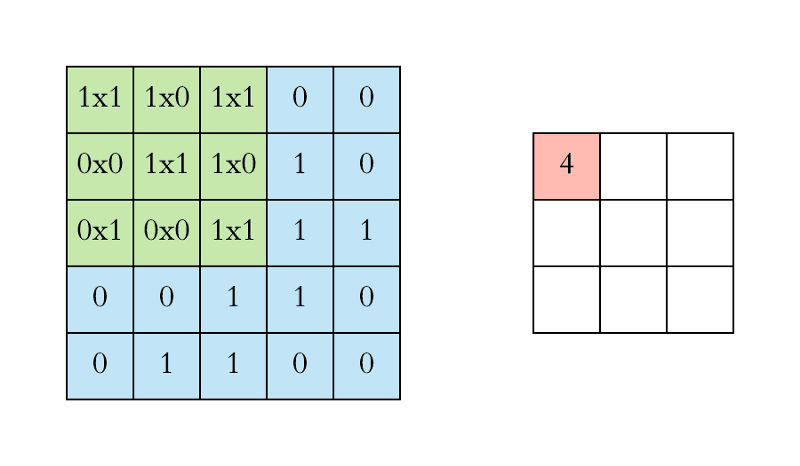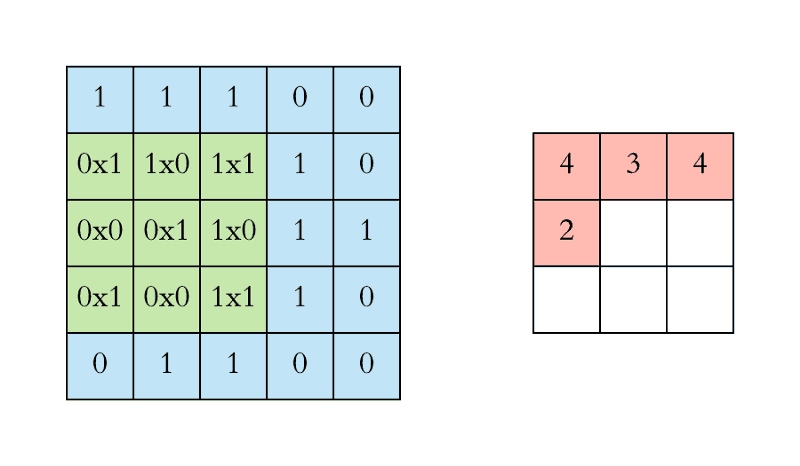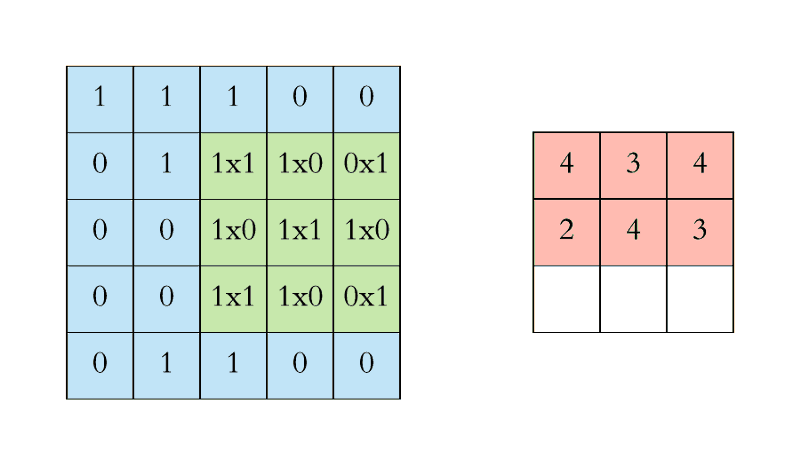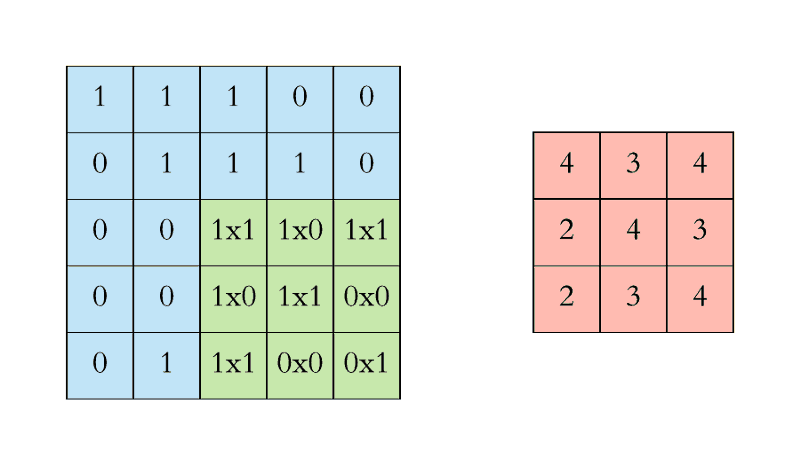
- In CNN, the convolution is performed on the input data with the use of a filter or kernel to produce a feature map.
- We execute a convolution by sliding the filter over the input.
- At every location, a matrix multiplication is performed and sums the result onto the feature map.
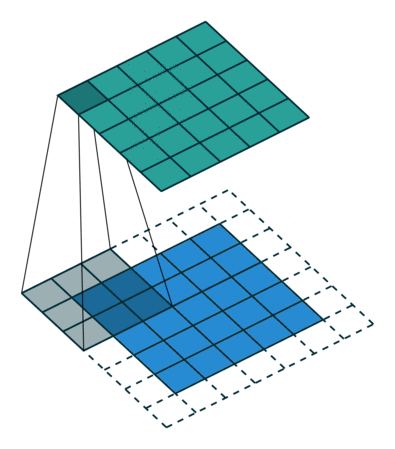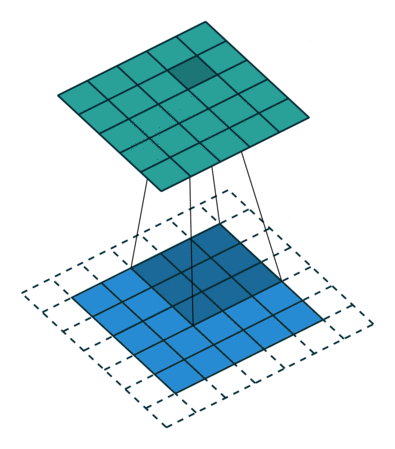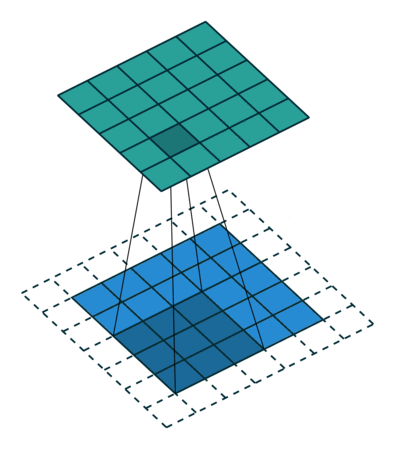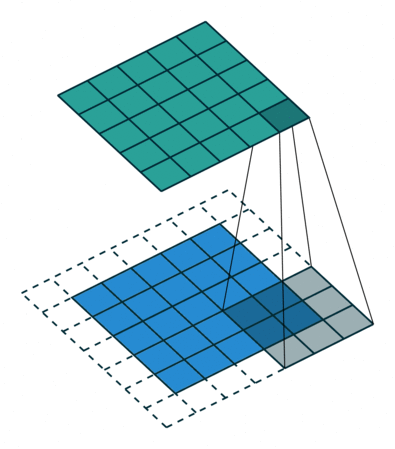
Stride
- Stride is the size of the step the convolution filter moves each time.
- A stride size is usually 1, meaning the filter slides pixel by pixel.
- By increasing the stride size, your filter is sliding over the input with a larger interval and thus has less overlap between the cells.
- Because the size of the feature map is always smaller than the input, we have to do something to prevent our feature map from shrinking. Here we use a technique called Padding.
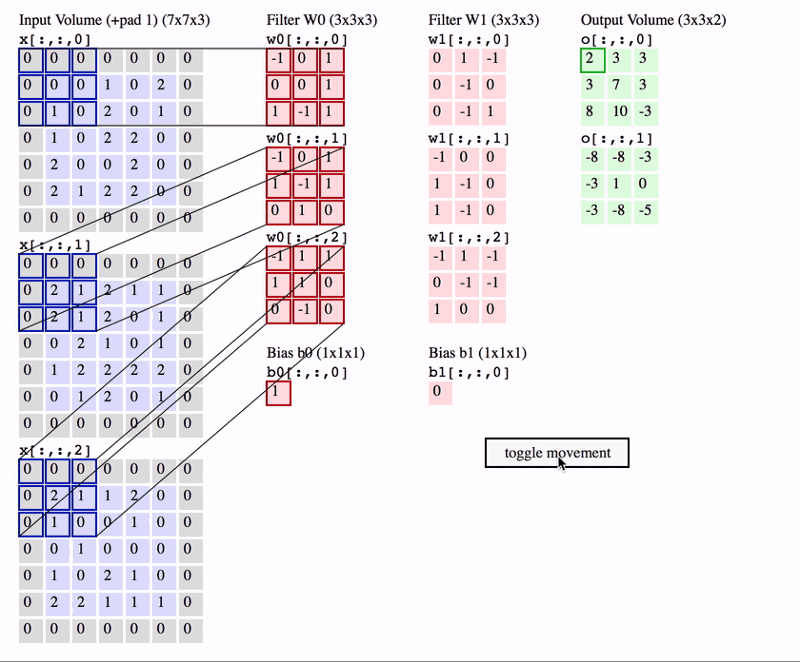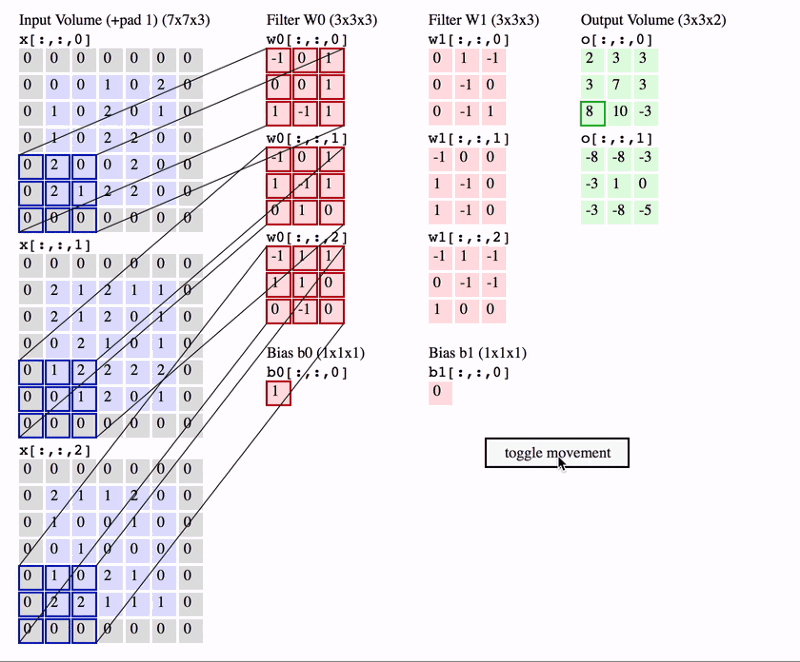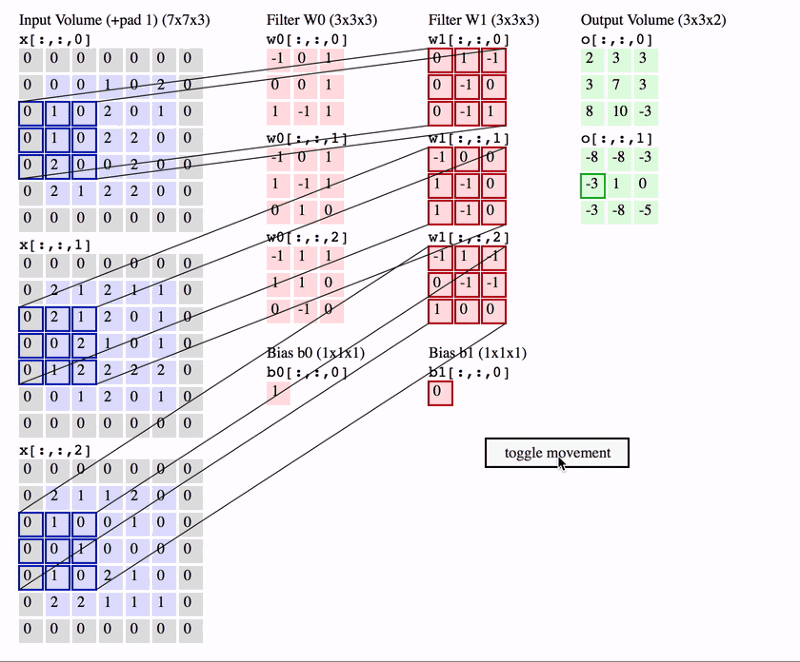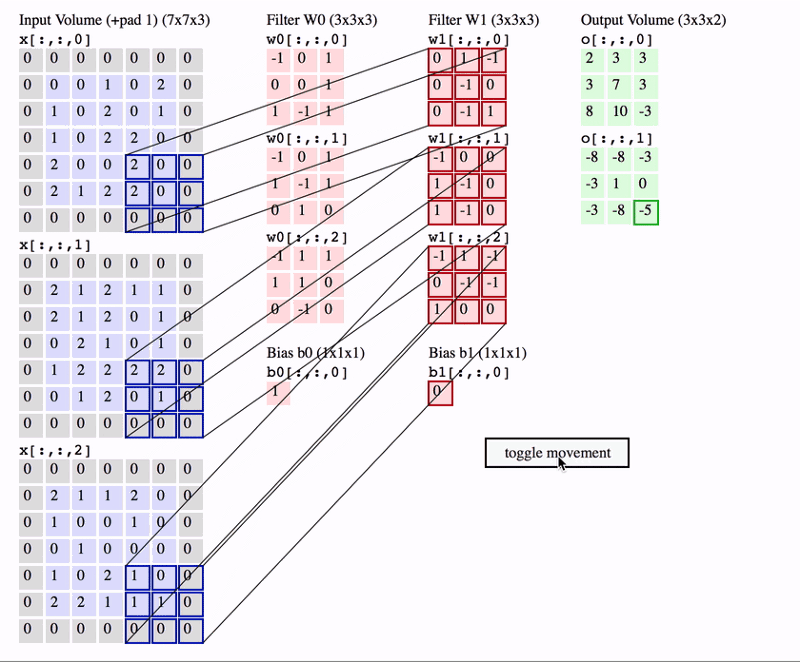
Padding
- Padding is adding a layer of zeros to surround the input to avoid shrinking of the feature map.
- In addition to keeping the spatial size constant after performing convolution, padding also improves performance and makes sure the kernel and stride size will fit in the input.
Classification Part
- A classification part consists of fully connected layers and these layers can accept 1-D data.
- Since we have 3-D data we use pythons flatten to convert that into 1-D data. The last layers of a Convolutional NN are fully connected layers.
- Neurons in a fully connected layer have full connections to all the activations in the previous layer.
- This part is in principle the same as a regular Neural Network.
Training CNN’s
- Training a CNN works in the same way as a regular neural network, using back propagation or gradient descent.
- However, in case of CNN’s it’s a bit more mathematically complex because of the convolution operations.
Conclusion
- The heart of the Convolutional Neural Networks is the technique called Convolution.
- A Convolution is where a filter slides over the input and merges the input value and then filter value on the feature map.
- The CNN uses back propagation or gradient descent as regular Neural Networks.