Keypoints
- Deep Learning(DL) is for everyone and it can be learned without starting with math.
- DL is good at lot of tasks such as Natural Language Processing, Computer Vision etc.
- It’s an technique to extract and transform data and it uses multiple layers of neural networks.
- Each of these layers take input from previous layers and refines them further. Over the time, the layers improve accuracy & minimize error. And the network learns to perform a specific task.
- Libraries like Fastai or pytorch may be outdated so its better to always learn the low level concepts & algorithms underlying.
- Machine Learning - Training of programs, developed by allowing a computer to learn from its experience, rather than manually coding the individual steps.
- Deep Learning - Its the more general discipline of machine learning.
- A general program takes inputs & outputs results.
- In machine learning the program is called Model since it takes inputs & weights.
- A Machine Learning program outputs results based on inputs & weights. The model can have a different outputs for same inputs with different set of weights.
- A Model is called trained when the weight assignment is final.
Important Note - Start
A Trained Model can be treated like a regular computer program. Neural Network - A flexible mathematical function that can be used to solve any problem.
In Neural networks, the way to automatically update weights for any given task is called “Stochastic Gradient Descent”. This process of going back and updating weights is called Back-propagation.
- The functional form of the model is called architecture.
- Weights / Parameters are interchangeable words.
- The actual results of the model are called “Predictions” and they are calculated from the independent variable, which is the data not including the labels.
- The way our model is performing, that measure is called “Loss”. In a dataset we have 2 things, 1. the Images & 2. the Labels. The labels are the categories or classes like cat or dog.
- The Labels are also called “Targets or Dependent variables” and the loss is dependent on the labels as well, not just solely on the predictions.
- Some of the limitations are: Model does not exist without data, model learns from the input data and the outcome is “predictions”.
- Some of the key functions/points learned out of fastAI library:
- untar_data() - A function that takes the url of the data set, downloads it and unzip it. In FastAI for Images, we have functions starting with Images like ImageDataLoaders and for text we have functions starting with Text like TextDataLoaders.
- In FastAI we have 2 types of transforms, Item transforms(item_tfms), and the other is Batch transforms(batch_tfms). The item tranformation operates on each item / input image to resize them to a similar size and the batch transform operates on the batches of items and pass them to the GPU(s) for training.
- And “EPOCH” is a one pass through, of all the images in training. And the process of the model learning in each epoch is called “Model Fitting”.
First Model as described in chapter 1
| |
- ImageDataLoaders function (Understanding each parameter)
- label_func: Takes a function as input, which is used for the classifying the outcome like Yes/No.
- Example : def is_cat(): return x[0].isupper(). A specific example since in this dataset of cats vs dogs the cats start with Uppercase and dogs with lowercase.
- item_tfms: Item Transformations - The item transform takes an Resize(224) input and transforms each image aka item into 224x224 size from what ever the original size of the each image might be.
- valid_pct: A valid percentage is required to split the data into training & validation. A validation set is critical for testing the model for what it has learned in the training phase from rest of the training data.
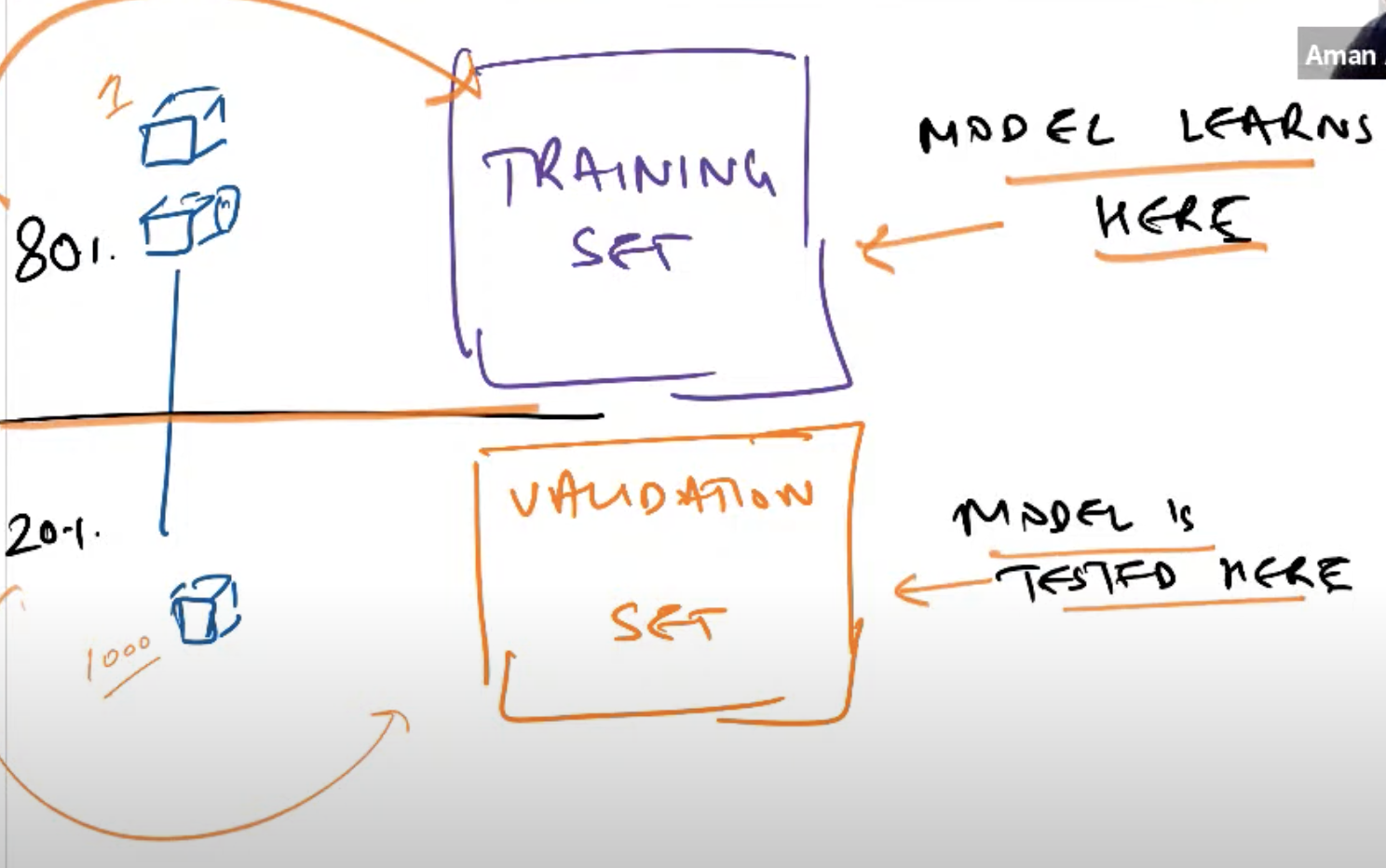 Image credits1
Image credits1
- Based on the predictions on the validation set(Hold-on set) , we can measure the performance of the model and also avoid overfitting.
- seed() - sets the seed value so that we get the same validation set every time we run the Model.
- cnn_learner function: A Convolutional Neural Network is a type of model that is best for vision based tasks and learns from the data. This method takes a particular type of architecture for example resnet34(34-layers) which is a mathematical model that can classify things.
- Overfitting - A concept thats occurs when the model fits exactly against the training data. In other words if the model tries to fit too closely to each point in the data, then the model becomes “overfitted”. And because of this overfitting model will be unable to generalize well to new data.
- Metrics - A metric is a function that measures how good the model predictions are comparing the output with actual label and is called Accuracy.
- Loss vs Metrics - A Loss is used by model for improving the training performance by updating weights using methods like SGD(using back-propagation) and Metrics is just a measure for us to know the performance of the model.
- Transfer Learning - Using a pre-trained dataset like IMAGENET for classifying a different task. A IMAGENET is an original dataset with 1M images used for vision tasks.
- Pre-trained weights - We use the weights from the pre-trained model and use that for our task. In this context the last layer is just updated with the new head (head - is our categories like cat & dog). That last layer replaced originally contained 1000 categories and now has just 2 categories.
- Fine Tuning - Training the model on a general dataset & then training it on our own dataset. This is where we are using the pre-trained weights for all the layers unaltered except for the last layer(head). The process of retaining the model stem(pre-trained weights) and just training the new head is called Fine Tuning. And it’s a Transfer learning technique.
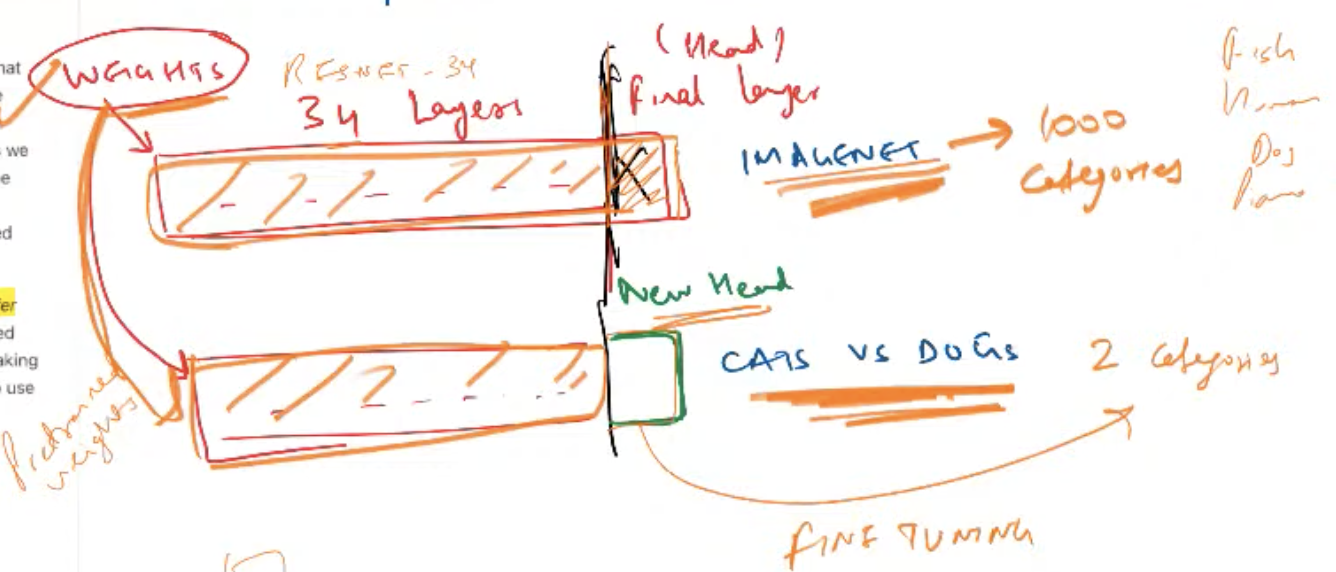
The fine tuning in Fast AI has 2 passes, in the first pass the pre-trained stem is frozen and the Head(the last layer / our data layer) is trained. And in second pass the stem & the trained head from first pass is again trained but at different speeds (trained head is again trained faster than the stem in this phase).
learn.fine_tune() - The number of times we want that pass to go through. If the no.of.epochs = 1, then each pass goes exactly once in the fine tuning steps. The Higher the epochs, the model learns better.
Model Learning - Demystifying Model Learning
- Each layer of the Model (each layer of the neural network : example 34 layers in restnet34) learns differently & different kinds of input patterns and by the last layer the model will be able to actually understand the task that we are aiming for.
- The best example of the how model learns after each layer is described in the paper by Matthew D. Zeiler & Rob Fergus2
- One of the Key idea in Computer Vision is to use the Pretrained weights since learning with lots of data in the stem gives the knowledge of shapes, sizes and all sort of information for the neural network and the last layer which is trained on our data knows how to recognize cats vs dogs. This also reduces lot of compute.
- Image Recognition can also handle non-image related tasks by converting the graphs & charts into images and then try identifying the patterns from those images.
Appendix
All Image credits to AmanArora from FastAI book reading session ↩︎
The above paper is from Matthew D. Zeiler & Rob Fergus. ↩︎